Trinidad is known for its vibrant musical traditions, which reflect the island's ethnic diversity. Soca is a dance music derived from calypso, a music with African antecedents. In parang, a Venezuelan and Spanish derived folk music that dominates Trinidadian Christmas festivities, groups of singers and musicians progress from house to house, performing for their neighbours. Chutney is an Indo-Caribbean music; steel drums are a Trinidadian invention. The annual Carnival, far and away the biggest event in Trinidad, is filled with soca and calypso music. In "Bacchanalian Sentiments", Kevin K. Birth argues that these and other Trinidadian musical genres and traditions not only provide a soundtrack to daily life on the southern Caribbean island; they are central to the ways that Trinidadians experience and navigate their social lives and interpret political events.Birth draws on fieldwork he conducted in one of Trinidad's ethnically diverse rural villages to explore the relationship between music and social and political consciousness on the island. He describes how Trinidadians use the affective power of music and the physiological experience of performance to express and work through issues related to identity, ethnicity, and politics. He looks at how the performers and audience members relate to different musical traditions. Turning explicitly to politics, Birth recounts how Trinidadians used music as a means of making sense of the attempted coup d'etat in 1990 and the 1995 parliamentary election, which resulted in a tie between the two major political parties. "Bacchanalian Sentiments" is an innovative ethnographic analysis of the significance of music, and particular musical forms, in the everyday lives of rural Trinidadians.
Update RequiredTo play the media you will need to either update your browser to a recent version or update your Flash plugin.

Dragon Ball Hit Song CollectionVarious ArtistsNippon Columbia

Brown Spirits#1Soul Jazz Records

Brown Spirits#2Soul Jazz Records

Brown Spirits#3Soul Jazz Records

Rebel Island SoulUnder the Influence: Reggae, Funk & Soul in Jamaica in the 1970sSoul Jazz Records

Glenn UndergroundAtmosfear (35th Anniversary Edition)Peacefrog

Glenn UndergroundThe Jerusalem EP’s (35th Anniversary Edition)Peacefrog

Terry CallierAt The Earl Of Old TownTime Traveler

Paul JohnsonBump Talkin’ (35th Anniversary Edition)Peacefrog

Paul JohnsonFeel The Music (35th Anniversary Edition)Peacefrog
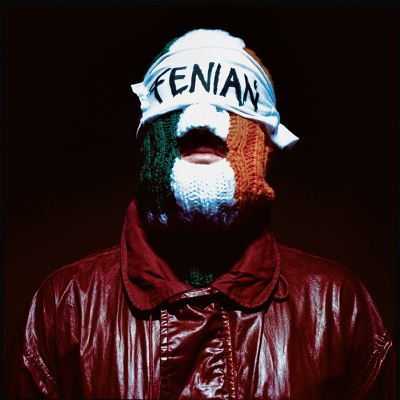

KNEECAPFENIANHeavenly Recordings

Roy Ayers UbiquityLive At The Montreaux Jazz FestivalUniversal Music Japan

Bulayo: Guitar Songs from Tanzania, Kenya, Zambia, and DR CongoVarious ArtistsMississippi Records

Adrian YoungeYoungLinear Labs

Eccentric Sweet SoulVarious ArtistsNumero Group

Rickey KellyMy Kind of Music (1979)Jazzman

Fred JacksonHootin’ ‘N Tootin’Blue Note

Nightmares On Wax vs Adrian SherwoodIn A Space Outta DubWarp Records

Nightmares On WaxIn A Space Outta Sound [20th Anniversary Edition]Warp Records

Larry YoungMother ShipBlue Note

John Lee HookerThat’s My Story: John Lee Hooker Sings the BluesConcord

Fight The Fire: Digital Reggae, Conscious Roots and Dub in Nigeria 1986-91Various ArtistsSoundway Records

Irreversible EntanglementsFuture, Present, PastVerve

Stan Getz & Luiz BonfáJazz Samba Encore!Verve

Ryuichi SakamotoOPUSSony

Frank SinatraSongs for Swingin’ Lovers!Blue Note

Black Jazz RecordsThe Best Of Black Jazz Records 1971-75Soul Jazz Records

Doug CarnThe Best Of Doug CarnSoul Jazz Records

Astrud GilbertoThe Shadow Of Your SmileVerve

Ranking BarnabasThe Cold CrusherJAMDUNG
YeBULLYgamma.

Pharoah SandersElevationVerve
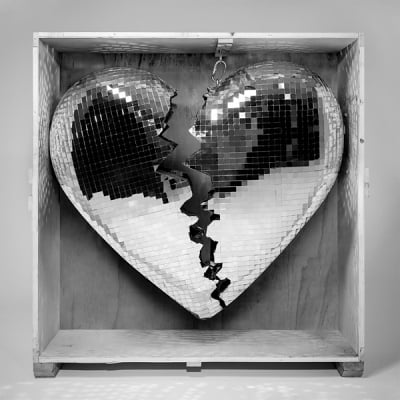

Mark RonsonLate Night FeelingsSony

The SkatalitesSka Authentic Vol. 2Studio One

The SkatalitesSka Authentic Vol.1Studio One
36421
Bacchanalian Sentiments Musical Experiences and Political Counterpoints in Trinidad
Duke University Press
- Book (400g) 9780822341659£20.00In stockAdd to Bag
Disenchanting Les Bon TempsIdentity and Authenticity in Cajun Music and DanceDuke University Press
CURRENTLY £72 ON AMAZON!!-------------------------------------
The expression laissez les bons temps rouler - 'let the good times roll' - conveys the...
- Book (400g) 9780822330202£25.00 £10.00In stockAdd to Bag
Tango LessonsMovement, Sound, Image, and Text in Contemporary PracticeDuke University Press
OVER 50% OFF THIS USA PAPERBACK. OVER £10 CHEAPER THAN AMAZON!--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
From...
- Book (650g) 9780822355663£21.99 £10.00In stockAdd to Bag
Musicians in TransitArgentina and the Globalization of Popular MusicDuke University Press
£10 OFF THIS USA NEW PAPERBACK. ALMOST £10 CHEAPER THAN AMAZON!!!----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------In...
- Book (550g) 9780822362364£22.00 £12.00In stockAdd to Bag
Made in NuYoRicoFania Records, Latin Music, and Salsa’s Nuyorican MeaningsDuke University Press
In Made in NuYoRico, Marisol Negrón tells the cultural history of salsa, tracing the music’s Nuyorican meanings over a fifty-year period that begins...
- Book (1kg) 9781478030898£23.99In stockAdd to Bag
Love Saves The DayA History Of American Dance Music Culture, 1970-1979Duke University Press
Essential, thorough book on the underground New York Disco scene of the 1970s written by Tim Lawrence (who also wrote the sleevenotes for Soul Jazz Records'...
- Book (800g) 9780822331988£24.00In stockAdd to Bag
Making SambaA New History Of Race and Music in BrazilDuke University Press
OVER 50% OFF THIS GREAT BOOK!! USA NEW PAPERBACK NEARLY £10 CHEAPER THAN AMAZON!!!-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
In...
- Book (700g) 9780822354307£25.00 £12.00In stockAdd to Bag
Songs of The UnsungBy Horace TapscottDuke University Press
£30 OFF !!!!! USA HARDBACK BOOK CURRENTLY £42 FOR THIS LOVELY HARDBACK ON AMAZON----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------"Songs...
- Book (600g) 9780822325314£45.00 £15.00In stockAdd to Bag
Contemporary Carioca: Technologies of Mixing in a Brazilian Music Sceneby Frederick MoehnDuke University Press
- Original Book (500g)£10.00Secondhand paperback ex-library in good condition.
100% Guarantee on this and all Original Books at Sounds Of The Universe - 'if you're not happy we're not happy' or your money back!In stockAdd to Bag
African RhythmsThe Autobiography of Randy WestonDuke University Press
OVER £10 OFF ORIGINAL PRICE !!! LOVELY USA IMPORT PAPERBACK BOOK! ONLY £12 SQUID - THAT's £10 CHEAPER THAN AMAZON!!!
Essential book - buy me!----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
The...
- Book (800g) 9780822347842£23.00 £12.00In stockAdd to Bag
Listening in DetailPerformances of Cuban MusicDuke University Press
£10 ONLY USA NEW PAPERBACK BOOK - £6 CHEAPER THAN AMAZON----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
"Listening...
- Book (550g) 9780822354581£16.99 £10.00New USA paperbackIn stockAdd to Bag
Rumba RulesThe Politics Of Dance Music In Mobutu's ZaireDuke University Press
OVER 50% OFF (THATS £13 OFF!) THIS GREAT USA NEW PAPERBACK BOOK - CHEAPER THAN AMAZON-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------Mobutu...
- Book (500g) 9780822341123£25.00 £12.00In stockAdd to Bag
BlutopiaGraham LockDuke University Press
In "Blutopia" Graham Lock studies the music and thought of three pioneering twentieth-century musicians: Sun Ra, Duke Ellington, and Anthony Braxton. Providing...
- Book (550g) 9780822324409£24.99In stockAdd to Bag











